Design Tools Used for Survey Topic Cyber Crime
Mini Review
Cyber Crime Awareness among Msw Students, School Of Social Work, Mangaluru
Department of Criminology and Forensic Science, School of Social Work, India
Submission: May 21, 2018;Published: May 30, 2018
*Corresponding author: Afrozulla Khan Z, Department of Criminology and Forensic Science, School of Social Work, Roshni Nilaya, Mangaluru, India, Email: aukhan2595@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Afrozulla K Z, Vaishnavi R T,Arjun . Cyber Crime Awareness among Msw Students, School Of Social Work, Mangaluru.J Forensic Sci & Criminal Invest. 2018; 9(2): 555757. DOI:10.19080/JFSCI.2018.09.555757.
Abstract
Cyber-crime also called Computer crime, the use of a computer as an instrument to further illegal ends, such as committing fraud, stealing identities, credit card fraud, spamming, password sniffers, and unauthorized access. The rapid growth of the internet and computer technology over the past few years has led to the growth in new forms of crime-dubbed cyber-crime throughout the world. The present study aims to find out the Cyber-crime Awareness among MSW students, School of Social Work, Mangalore. A questionnaire based survey method on cyber -crime awareness among MSW students was applied to analyze the awareness in the field of cyber-crime. For this purpose a sample of 100 MSW students was selected. This survey examines the MSW student's awareness about cybercrime and some suggestions are assign to control these cyber-crimes.
Keywords: Cyber-Crime; Msw Students; Awareness.
Introduction
Cyber Crime
This is any crime that involves computer and a network. In some cases, the computer may have been used in order to commit the crime and in other cases the computer may have been the target of the crime. The oxford reference online defines 'cyber-crime' as crime committed over the Internet. The encyclopedia Britannica defines 'cyber-crime' as any crime that is committed by means of special knowledge or expert use of computer technology. So what exactly is cyber-crime? Cyber-crime could reasonably include a wide variety of criminal offences and activities. A generalized definition of cyber-crime may be 'unlawful acts wherein the computer is either a tool or target or both'. The Cyber-crime can be generally defined as a criminal activity in which information technology systems are the means used for the commission of the crime (Figure 1). Cyber-crimes are of many types:
Computer Viruses: Computer Viruses are computer programs that, when opened put copies of themselves into other computers' hard drives without the users' consent. Creating a computer virus and disseminating it is cyber-crime (Table 1). The virus may steal disk space, access personal information, ruin data on the computer or send information out to the other computer user's personal contacts.
Cyber Stalking: Cyber Stalking is the use of the Internet to electronics to stalk or harass an individual, an organization or a specific group. There are many ways in which cyber stalking becomes a cyber-crime (Figure 2). Cyber stalking can include monitoring someone's activity real-time or while on the computer or device in the current moment or while they are offline, or not on the computer or electronic device. Cyber stalking becomes a crime because of the repeated threatening, harassing or monitoring of someone with whom the stalker has, or no longer has a relationship [1].
Identity Theft: Identity Theft is a form of stealing someone's personal information and pretending to be that person in order to obtain financial resources or other benefits in that person's name without their consent. Identity theft is considered as cybercrime (Table 2). The personal information stolen can include the person's name, social security number, birth date or credit card numbers. This stolen information is then used to obtain new credit cards, access bank accounts or obtain other benefits, such as driver's license. Identity theft is committed by using breaches in the victim's browser security or through spyware, which is software placed unknowingly on a person's computer in order to obtain information. Identity theft can also be performed by hacking into computer networks to obtain personal data- sometimes in large amounts [2].
Internet Crimes: Internet Crimes is crime committed on the Internet using the Internet and by means of Internet. Computer crime in general term, that embraces such crimes phishing, credit card frauds, bank robbery, illegal downloading, industrial espionage, child pornography, kidnapping children, via chat rooms, scams, cyber terrorism, creation or distribution of viruses, spam, and so on(Figure 3). All such crimes are computer related and facilitated crimes.
Awareness
Awareness an emotional reaction towards a person or thing is usually termed as Awareness. It is actually a personal response to an object, developed through experience which can be called favorable or unfavorable. Awareness may be towards concrete or abstract things (Table 3).
Awareness of Cyber Crime
Awareness of Cyber Crime could be defined as a compact term which expresses norms and crimes that are followed in the cyber space, or internet (Figure 4). Often the word cybercrime is used in context with varied meanings ranging from the crime of hacking or even computer revolution or even cyber cultural issues like cyber topics, cyber organization etc(Table 4). There are estimated 600 million mobile users and 130 million internet users in India along with 20 million broadband users [3]. Facebook reported that as of December, 2012, it has 71 million users in India and most of them are accessing Internet through mobile phones. These reports would tell how much the Indian youth has made internet communication mediums such as Google and Facebook part and parcel of their everyday affairs. But at the same time, it also needs to be understood that millions of internet users in India are unaware of cyber safety and security essentials, netiquettes and proper forums for reporting crimes. Internet and digital communication technology (DCT) has created an enormous opportunity for people of all ages including student community to contribute and accumulate information. People are getting connected to each other through emails, chat rooms, social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter etc. (Figure 5), blogs etc. Internet and DCT also make it possible for users to avail online banking, shopping as well as e-library facilities.
The purpose of this survey is, as we are living in 21st century which is called as an InfoTech age or computer age we should be well aware about the various aspects of the information technology and specially used by college students. The college students use computers to secure their important data however at the same time the various security aspects should be taken into consideration (Table 5). The various concepts of electronic communication are unaware to the college students because of lack of knowledge, lack of cyber-crime awareness and awareness towards use of Internet. The college students should be aware so as to secure the information which is preserved in electronic form. The Government should also take various steps pertaining to the protection of data (Table 6). The experts in information technology track the valuable information regarding defense and security of the nation. Such type of the act may threaten to the national and international peace. So as to protect the interest of nation we have to do research in such a field like cyber-crime awareness and attitude towards Internet. Due to the emergence of computer networking and development in the area of internet and its frequent use in cyber-crime, there are several issues and challenges that will be addressed in the current research (Figure 6).
Materials and Methods
Ethical Statement
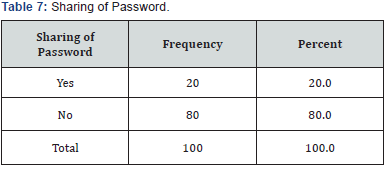
I hereby declare that this research project entitled "Cyber Crime Awareness among MSW students, School of Social Work, Mangalore" is a bona-fide research carried out by me and my copartner under the guidance of Mr arjun M. S, Assistant Professor, Department of Criminology and Forensic science, school of Social Work, Roshni Nilaya Mangalore. The present study aims to understand cyber-crime awareness among MSW students, School of Social Work, Mangalore (Table 7).
Objective
Any study must yield information which will be helpful for an individual or a group at large. Therefore, to reach out a particular conclusion and to find a solution it is essential to set the objectives. The objectives of the study are as follows:
a. To know the profile of respondents.
b. To recognize level of awareness on internet usage.
c. To recognize level of awareness on user information (User ID & Password).
d. To recognize level of awareness about Cyber-crime among the respondents
Problem Statement
The purpose of the research was to find out the knowledge of cyber and its terms among MSW students. As the cybercrime increasing day by day, there arises the need to improve the knowledge about cyber and to avoid being victim of the cyber-crime. The study was an attempt to find out whether the social work students are aware of cyber and its crime. The study can help management to know about the knowledge of MSW students in cyber (Figure 7).

Research Design
The research design is a conceptual structure within the research study is undertaken. The preparation of such design facilitates research to be as effective as possible yielding maximum information. Descriptive Research Design was employed for the study.
Scope Of The Study
The scope of the study is that people's perception and attitude towards computer safety and information security significantly affect the way they use information technology. The study is an attempt to understand perception of MSW students on security measures in cyber. The paper intends to examine the level of safety and security awareness among MSW students.
Universe Sample and Sampling Technique
For the purpose of this study, the first and second year MSW students of School of Social Work were taken as universe. In the present study, the term respondents are referred to MSW students of School of Social Work-Mangaluru. A small representation of the larger whole population is studied. The selected respondents are technically called 'sample' and the selection process is called 'sampling techniques'. For the purpose of the study the investigator has selected 100 MSW students. The sample was selected through 'Simple Random Sampling Method'. The MSW students were randomly chosen as respondents. Age of the respondents was distributed from 20-35 years. Written consent was taken from all participants (Figure 8).
Tools of Data Collection
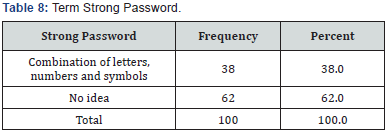
A tool is an aid with necessary and relevant information that could be gathered systematically to the subject matter. The tool was decided on the basis of the objectives of the study (Table 8). The Questionnaire method was the tool of data collection, which was used by the researchers for the purpose of collecting data from the respondents. Questionnaire method is the best method for collecting the maximum information in a systematic method. The researcher has used a combination of open optional and close ended questions.
Data Collection and Procedure
The study is based on primary data and the information for the present study was collected from 100 respondents (MSW - first and second year students) of School of Social Work-Mangaluru. The data was collected by simple random sampling method. Opinion and views of the respondents were collected through the Questionnaire method. The investigator after building an understanding with the respondents described the purpose, importance and significance of the study. The questionnaire was filled in the presence of researchers so that researchers could clarify the doubts of respondents regarding the questions.
Results and Discussion
The age of the respondents, 72% of the respondents belong to age group of 21-23 years. 16% of the respondents belong to age group of >26 years. 11% of the respondents belong to age group of 24-26 years. Only 1% of the respondents belong to age group of 20 years (Figure 9).
Awareness on Internet Usage
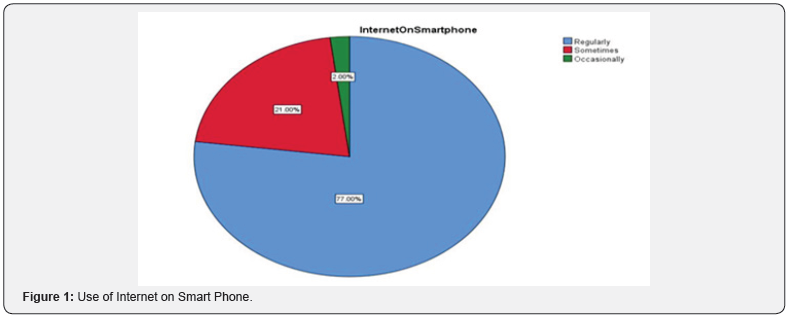
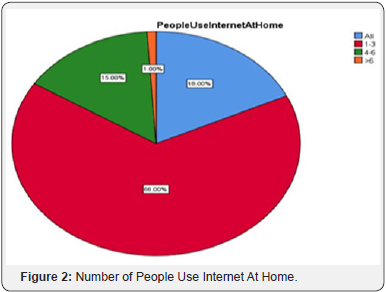
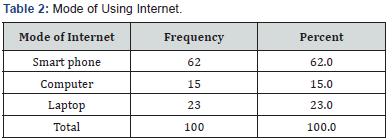
Respondents were asked about mode of using internet, 62% of the respondent's access internet in smart phone, 23% respondent's access internet in laptop and remaining 15% respondents access internet in computer. Respondents were asked about use of internet on smart phone, 77% of the respondents use the internet on smart phone regularly, 21% uses internet on smart phone occasionally and only 2% of the respondent uses internet sometimes. 66% of the respondent stated that 1-3 members in the family use internet, 18% of the respondent stated that all members in the family use internet, 15% of the respondent stated that 4-6 members in the family use internet, 1% of the respondent stated that more than 6 members in the family use internet. Respondents were asked about usage of internet, 93% of the respondents access the internet at least once a day highlighting the attraction of the respondents towards the internet, 6% of the respondents uses internet once in a week, only 1% respondents use internet once in a month (Figure 10).
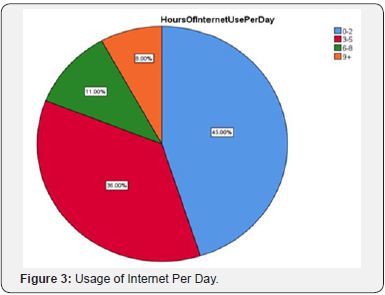
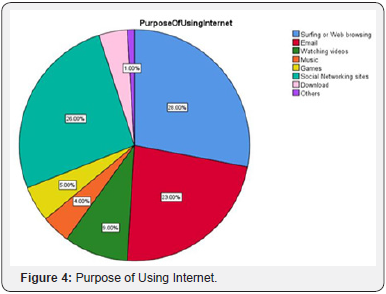
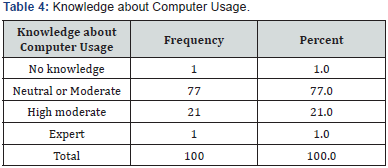
Respondents were asked about usage of internet per day, 45% respondent's uses internet 0-2 hours per day, 36% uses internet 3-5 hours per day, 11% of the respondents uses internet for 6-8 hours per day and 8% of the respondents uses internet for 9+ hours per day. The purpose of using internet for surfing or web browsing was 28%, the other common activities like Email was given as 23%, Watching videos as 9%, games as 5%, Social networking sites as 26%, download as 4% and others as 1%. Respondents were asked about computer usage knowledge, 77% respondents have neutral or moderate knowledge of computer, 21% of the respondents have high moderate knowledge about computer usage, and about 1% respondents are expert and 1% has no knowledge about the usage of computer (Table 9).
Awareness On User Information (User Id & Password)
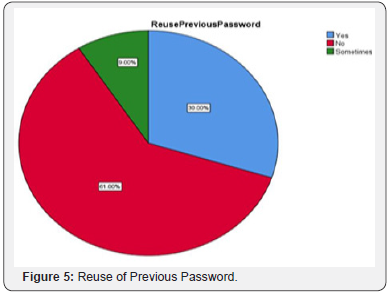
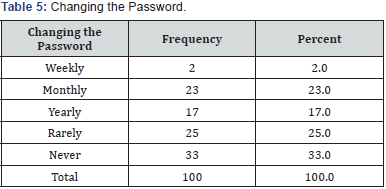
Respondents were asked about changing the password, 33% of the respondents never change their password, and 25% of the respondent changes their password rarely, 23% of the respondents changes their password monthly, 17% of the respondents change their password once in a year, and few of the respondent that is 2% changes their password once in a week. Respondents were asked about reuse of previous password, 61% result shows that the respondents never use the old or previous password when they change the password to new, about 30% of the respondent reuses their password and 9% respondents uses sometimes. 47% result shows that the respondents use same password for each account, and 52% respondents do not use same password, minority of the respondents i.e., 1% use the same password for each of their account (Figure 11).
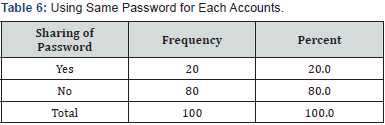
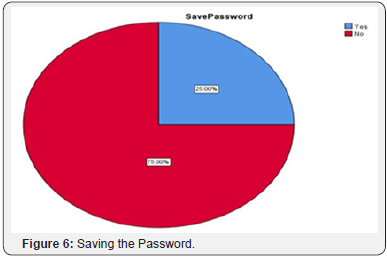
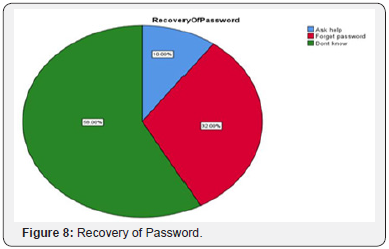
80% of the respondent will never share password, and only 20% of the respondents share their passwords. Respondents were asked about saving the password, 75% of the respondents never save their password if the computer or smart phone prompts to save password, and 25% do attempt to save. Majority 92% of the respondent never use the password found in password dictionary, 8% of the respondents use password which is found in dictionary. Majorities 58% of respondents don't know how to recover their password, 32% of the respondents answered as forget password, 10% of the respondents ask for help. Respondents were asked about strong password, 62% of the respondent don't know what is meant by strong password. This shows most of the people use mobile numbers, names, date of birth as their password, 38% of the respondents understand the term strong password by combination of letters, numbers and special characters (Table 10).
Awareness on Cyber Crime
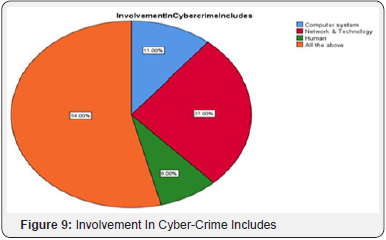
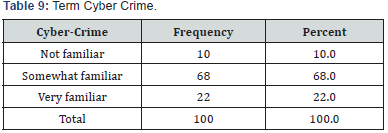
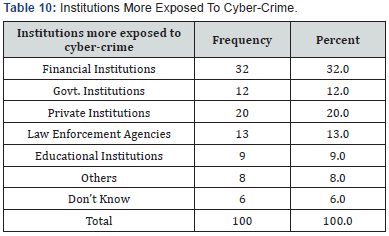
Respondents were asked about term cybercrime, 68% respondents stated that they are somewhat familiar with the term cyber-crime, 22% of the respondents are very familiar with the term cyber-crime, and 10% of the respondents are not familiar with the term cyber-crime. 27% of the respondents think involvement in cyber-crime includes Network & Technology, 11% of the respondents think involvement in cyber-crime includes Computer System, 8% of the respondents think involvement in cyber-crime includes Human. 54% of the respondents answered all the above which includes Computer System, Network and Technology and human. Majority 32% of the respondent optioned that financial institutions are exposed more to cyber-crime.
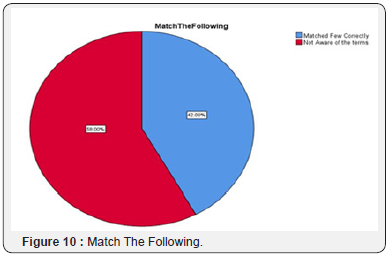
20% are private Institutions, 13% are Law Enforcement Agencies, 12% are Government Institutions, around 9% are Educational Institutions, 8% as Others, and minority of respondents that is 6% are not aware of it. The respondents were asked to match the particular definitions like, Unauthorized Access, Email Bombing, Data Diddling, Internet Time Theft, Password Sniffers, Spamming, Cyber Stalking, Credit Card Fraud, Identity Theft, and Phishing Attack. 58% of the respondents are not aware of these terms and 42% of the respondent matched one or two correctly The respondents have not come across any cyber-crime related cases, few respondents answered Yes but they did not mention the type of Cyber-Crime, which shows that they are not aware of that particular crime. Respondents were asked about reporting cybercrimes, All the respondents do not have fear of reporting cyber-crimes (Figure 12).
Conclusion
On the basis of findings of present work, it could be concluded that there is a significant difference between the awareness level of different age group. Results revealed the importance of awareness as a tool to decrease/ prevent cybercrime. The overall findings indicate unsatisfactory awareness on cyber-crime among MSW students. Therefore, it is concluded that the hypothesis has not been proved to be coherent, i.e., MSW students are not aware of cyber-crimes.
Acknowledgement
First and foremost, we would like to thank God Almighty for showering his choicest blessings, which has helped us to make this research reality. It is with pleasure that we record our indebtedness to our academic Guide, Mr. Arjun M S, Lecturer, Post Graduate Department of Criminology and Forensic Science, School of Social Work, Mangaluru for his guidance during the preparation of this minor research. We would like to thank Ms. Saritha D'Souza, Head and Ms. Bhavyashree Rai, Lecturer, Post Graduate Department of Criminology and Forensic Science, School of Social Work, Mangaluru, for their constant support in our research work. Our sincere thanks to Dr. Sophia N. Fernandes, Principal, School of Social Work, Mangaluru, for giving us the opportunity to undertake this study. We sincerely thank Dr. Meena Monterio, Head of the Post Graduate Department of Social Work, School of Social Work, Mangaluru, for helping with data collection. We sincerely thank participants for their support and cooperation during data collection. We would like to thank our family for the constant encouragement and support throughout our life and academic career.
References
- Bijoy Saima (2015) Cyber Crime Awareness amongst students of Government Law College Trivandrum-A Leagal survey.
- Ali MM (2016) Determinants of Preventing Cyber Crime: a Survey Research. International journal of Management Science and Business Administration 2(7): 16-24.
- Mehta S, Singh V (2013) A study of awareness about Cyber Laws in the Indian Society. International Journal of Computing and Business Research (IJCBR) 4(1): 334.
Design Tools Used for Survey Topic Cyber Crime
Source: https://juniperpublishers.com/jfsci/JFSCI.MS.ID.555757.php
0 Response to "Design Tools Used for Survey Topic Cyber Crime"
Post a Comment